Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Impact of 3D Printers on Business
In recent years, the advent of 3D printers has marked a significant shift in the landscape of manufacturing and production. This innovative technology allows businesses to transition from traditional manufacturing processes to a more streamlined, cost-effective, and customizable approach. By harnessing the power of 3D printing, companies can create prototypes, reduce waste, and simplify their supply chains. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the transformative impact of 3D printers on various sectors of the business world, their applications, advantages, and future potential.
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, refers to the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This is achieved by laying down successive layers of material until the entire object is built. The materials used can range from plastics to metals and even biological materials. The most commonly used 3D printing methods include:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): This is the most popular and widely used 3D printing technology. It works by extruding melted thermoplastic filament through a heated nozzle to form layers.
- Stereolithography (SLA): This method utilizes a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a layer-by-layer fashion.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): In this technique, a laser fuses powdered material, which could be plastic, metal, or glass, to create a solid structure.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA, but instead of using a laser, it projects a digital light image onto the resin layer to cure it.
The Advantages of 3D Printers in Business
The integration of 3D printing technology into business operations offers numerous benefits that traditional manufacturing methods cannot match. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of 3D printing is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional manufacturing often requires expensive molds and tooling, which can be prohibitive for small series production. With 3D printers, companies can produce items on demand without the need for such costly investments. This reduction in overhead costs allows businesses to allocate their resources more efficiently.
2. Rapid Prototyping
3D printers enable businesses to produce prototypes quickly and efficiently. Designers and engineers can create and test their products in-house, allowing for faster iterations and modifications based on immediate feedback. This accelerated development process can significantly reduce time-to-market, giving companies a competitive edge.
3. Customization and Personalization
In today's market, customization is paramount. 3D printing allows businesses to tailor their products to meet specific customer demands. Whether it’s bespoke jewelry or custom-fit medical devices, the ability to personalize products enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
4. Sustainability
Sustainability is a growing concern for consumers and businesses alike. Traditional manufacturing processes often result in significant waste, as materials are cut away from larger stock pieces. 3D printing, by contrast, is an additive process that uses only the material needed to create an object, resulting in minimal waste. Furthermore, the ability to produce parts locally can significantly reduce transportation emissions.
5. Supply Chain Simplification
3D printing can simplify supply chains by eliminating the need for extensive inventories and reducing lead times. Businesses can print components and products as needed, minimizing storage costs and the risk of overproduction. This level of agility allows companies to respond quickly to market demands.
Applications of 3D Printing in Various Industries
The versatility of 3D printers has led to their adoption across various industries, each benefitting from this revolutionary technology in unique ways:
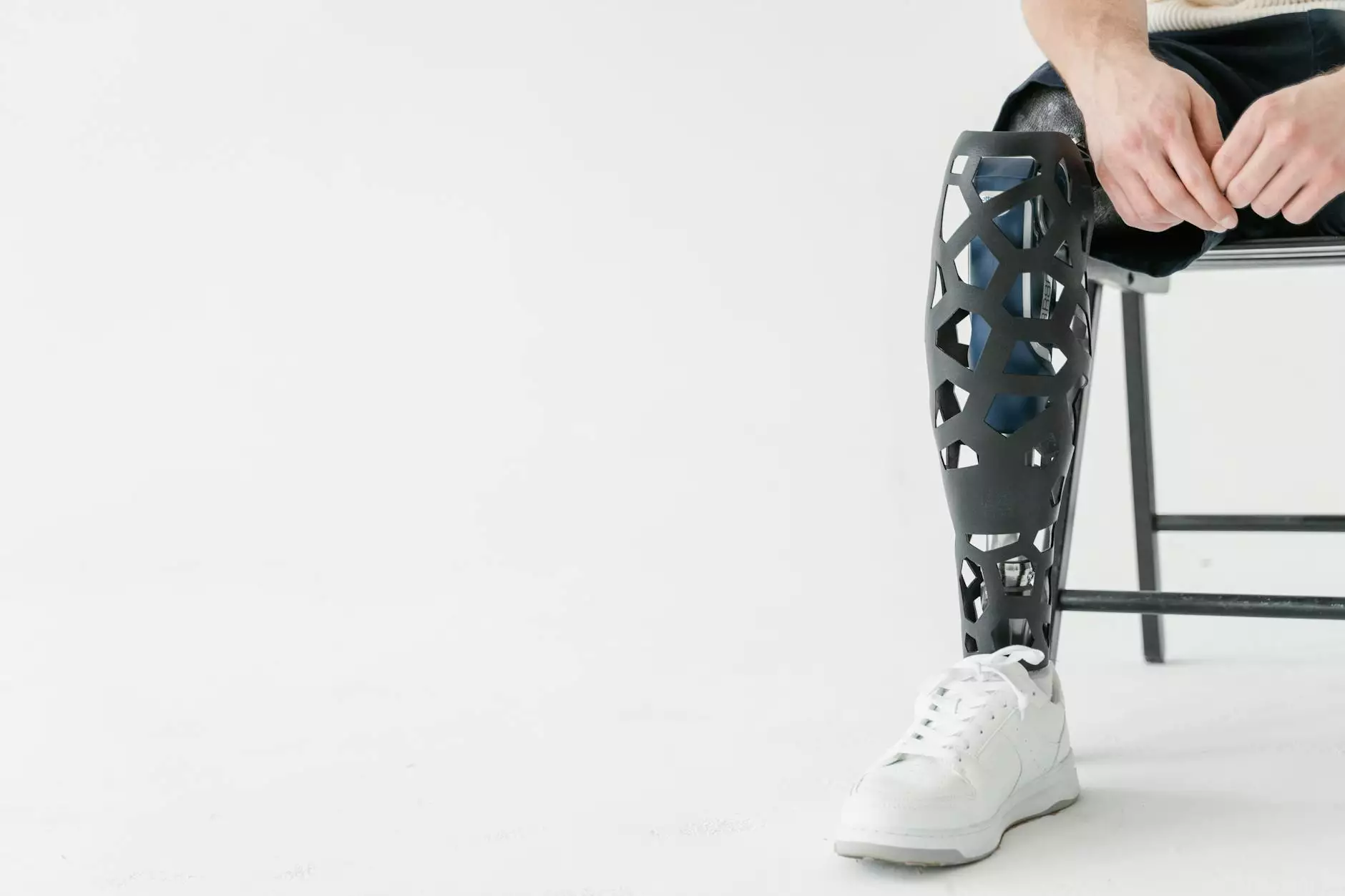
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, 3D printing is making waves through applications such as creating patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and even bio-printed tissues. Surgeons can now use 3D printed models of patients' organs to plan surgeries, leading to improved outcomes.
2. Automotive
The automotive industry has embraced 3D printing for producing lightweight components, prototyping new designs, and even creating tools for assembly lines. Companies like BMW and Ford are leveraging 3D printing to innovate faster while reducing production costs.
3. Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on 3D printing for creating high-strength components while minimizing weight. This technology has been instrumental in manufacturing engine parts and complex components that traditional methods cannot produce.
4. Consumer Products
Businesses producing consumer products utilize 3D printers to create prototypes and final products that meet specific customer preferences. Brands like Adidas and Nike have started using 3D printing technology to create customized footwear, providing a unique competitive advantage.
5. Education
In education, 3D printing serves as a valuable tool for teaching design, engineering, and technology concepts. Schools and universities are integrating 3D printers into their curricula to foster creativity and hands-on learning among students.
Future Trends in 3D Printing
The future of 3D printing is promising, with numerous trends indicating continued growth and innovation. Some of the most anticipated developments include:
1. Advancements in Materials
As 3D printing technology evolves, the range of available materials is expanding. New composites and bio-materials are being developed, enhancing the applications of 3D printers in various fields.
2. Increased Automation
Automation will play a crucial role in the future of 3D printing. Incorporating robotics into the printing process will enhance production speed and efficiency, enabling mass customization without slowing down output.
3. Integration with AI and IoT
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) with 3D printing technology will lead to smarter production processes. AI can optimize designs for better performance and operational efficiency, while IoT can facilitate real-time monitoring and management of 3D printing systems.
4. Sustainable Practices
The emphasis on sustainability will shape the future of 3D printing. Businesses will increasingly seek eco-friendly materials and practices, driving innovations in recycling and the use of biodegradable materials.
5. Expanding Market Accessibility
As 3D printers become more affordable and user-friendly, we can expect a surge in small businesses and individual entrepreneurs utilizing this technology. Democratizing access to 3D printing will foster innovation and creativity across various sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printers are not just a passing trend; they signify a fundamental change in how businesses approach manufacturing and product development. The impact of 3D printing on cost savings, rapid prototyping, customization, sustainability, and supply chain efficiency is profound. As technology continues to evolve, we can anticipate even more incredible applications and innovations that will shape the future of industries worldwide.
For any business looking to stay ahead in the competitive landscape, investing in 3D printing technology is not just an option; it’s a necessity. By embracing 3D printers, companies can unlock new possibilities, drive innovation, and meet the ever-changing demands of their customers.
For more insights on the impact of 3D printing in business, feel free to visit us at infotron.com.tr.



